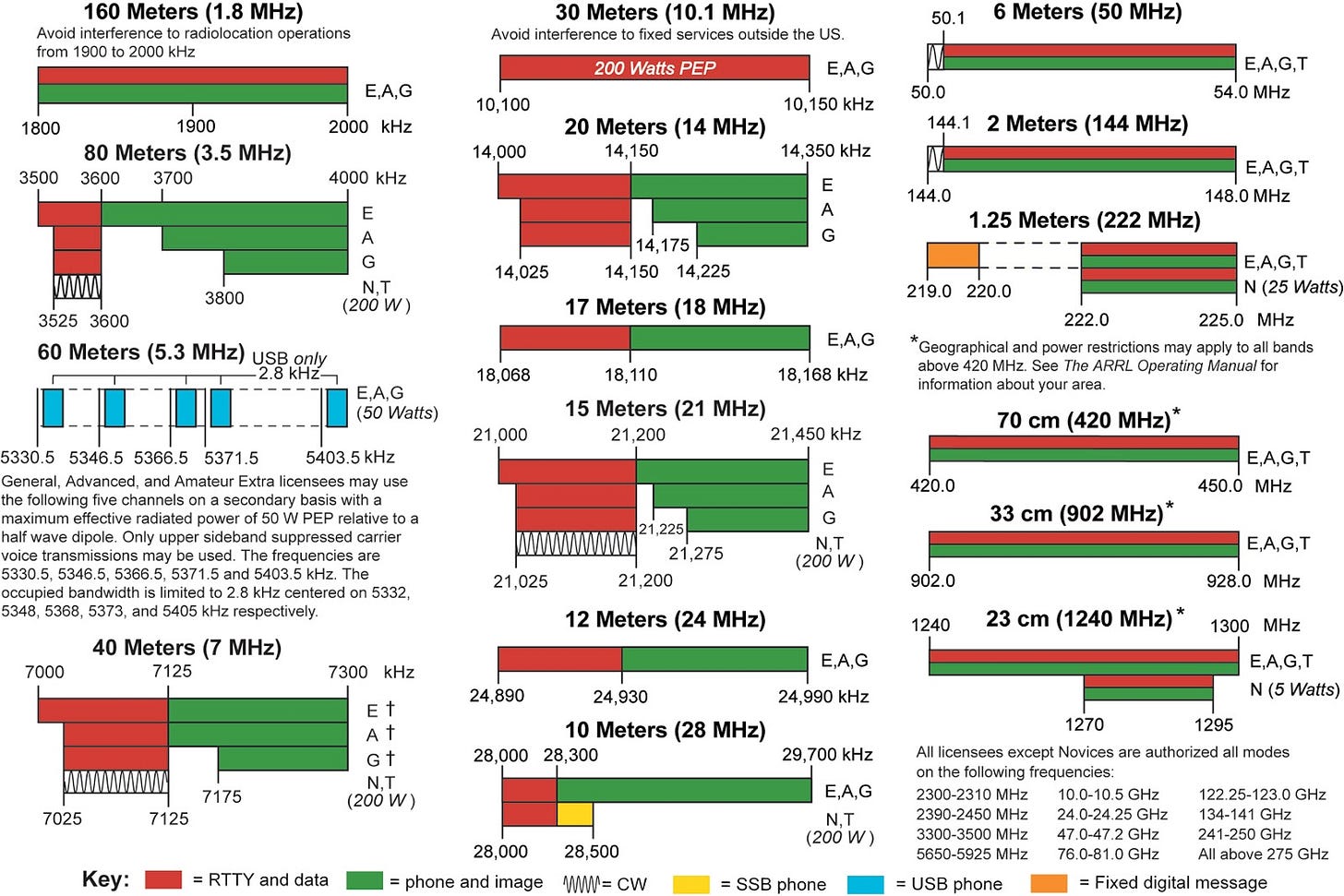
Understanding Ham Radio Bands
Ham radio bands are portions of the radio spectrum allocated for amateur radio use. Each band corresponds to a specific range of frequencies, typically identified by wavelength in meters or by frequency in megahertz. Lower frequency bands have longer wavelengths and tend to travel farther, especially at night, while higher frequency bands often allow for local or line-of-sight communication with less interference.
The characteristics of a band are shaped by several factors:
Wavelength: Longer wavelengths travel farther and bend around obstacles better.
Propagation: How signals reflect, refract, or are absorbed in the atmosphere.
Time of Day: Some bands work best during daylight, others at night.
Solar Activity: Higher solar activity can enhance high-frequency propagation.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Amateur Radio Today to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.